There are no unimportant vitamins or minerals in the body; each performs a specific function. Zinc is no exception. Since the human body cannot synthesize it, consuming zinc through food or supplements is essential for maintaining overall health. In this article, with Herbzone, we’ll explore zinc’s role, indications for supplementation, deficiency symptoms, and usage recommendations, along with a list of the top 5 zinc supplements from iHerb.
In This Article:
- The Role of Zinc in the Human Body
- Indications for Zinc Supplementation
- What Are the Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
- Which Foods Naturally Contain Zinc
- Recommended Daily Zinc Intake
- Choosing and Taking Zinc Supplements
- Side Effects and Overdose Risks
- Top 5 Zinc Supplements from iHerb
The Role of Zinc in the Human Body
Before selecting supplements, let’s understand why zinc is beneficial and why it’s necessary. This trace element is involved in numerous vital bodily processes. It is essential for immune system function and supports healthy skin, hair, nails, and vision. Additionally, zinc plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels, aiding in the prevention of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Key Benefits of Zinc:
- Immune System Support: Enhances lymphocyte activity and helps combat infections.
- Problematic Skin and Acne: Regulates sebum production to reduce acne and exhibits antibacterial properties to fight acne-causing bacteria.
- Wound Healing: Stimulates tissue regeneration and improves the function of enzymes responsible for wound healing and scar reduction.
- Brain Function: Adequate zinc levels are associated with better memory, cognitive abilities, and reduced risk of depression.
- Hair and Nail Health: Supports hair and nail growth, preventing brittleness and loss.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Participates in insulin synthesis and secretion, improving sensitivity and glucose control.
- Eye Health: Prevents age-related vision decline, including macular degeneration, and maintains visual sharpness.

Indications for Zinc Supplementation
Zinc supplements provide health support across various areas, from strengthening the immune system to enhancing reproductive health and preventing chronic diseases. Who needs zinc supplementation?
- Chronic Diseases: Recommended for osteoporosis, macular degeneration, and diabetes to improve metabolism, strengthen bones, and reduce oxidative stress.
- Reproductive Health: Essential for hormone production, improving sperm quality in men, and supporting a healthy menstrual cycle in women.
- Children with Persistent Diarrhea: Zinc aids nutrient absorption, prevents dehydration, and restores intestinal health.
- Skin Conditions: Effective in treating acne, eczema, and other skin issues due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Age-Related Disease Prevention: Helps lower the risk of neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s, supporting brain health.
- Digestive Health: Promotes the production of digestive enzymes essential for protein and nutrient absorption.
- Hair and Nail Support: Prevents hair loss and brittle nails while promoting healthy growth.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Improves insulin function and reduces inflammation in diabetic patients or those at risk.
- Bone Strength: Necessary for maintaining bone density, particularly in older adults or those at high risk of osteoporosis.

What Are the Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
Zinc deficiency can affect various aspects of health since this trace element is involved in many bodily processes. Its lack often manifests in noticeable symptoms that require attention and correction.
- Hair Loss
Zinc is essential for normal hair growth. A deficiency may lead to brittleness, slowed growth, and hair loss. - Nail Dystrophy
Nails become brittle, and white spots or deformities may appear, signaling metabolic issues. - Frequent Colds
Without adequate zinc levels, the body struggles to fight infections and recover from illnesses. - Developmental Delays in Children
Zinc deficiency in children may result in slowed growth, impaired cognitive abilities, and reduced appetite. - Skin Problems
Symptoms may include rashes, irritation, or delayed wound healing. - Loss of Appetite
Zinc deficiency affects taste receptors, leading to a decreased appetite. - Vision Issues
Lower zinc levels can impair vision, particularly in low-light conditions. - Chronic Fatigue
A lack of zinc may cause general weakness and quick fatigue.

Which Foods Naturally Contain Zinc
Zinc can be obtained from many readily available and healthful foods. Including them in your daily diet is essential to ensure sufficient levels of this trace element.
- Seafood
Oysters, crabs, and shrimp are excellent sources of zinc. - Red Meat
Beef and lamb contain high levels of this element. - Poultry
Chicken and turkey are also good sources of zinc. - Legumes
Beans, chickpeas, and lentils are rich in zinc. - Nuts and Seeds
Pumpkin seeds, almonds, and cashews help replenish zinc levels. - Whole Grains
Oatmeal, brown rice, and whole-grain bread are great options. - Dairy Products
Cheese, yogurt, and milk contain zinc. - Eggs
Chicken eggs provide a small but significant amount of zinc. - Leafy Greens
Spinach and other leafy vegetables serve as additional zinc sources.
Zinc from food is absorbed differently based on its source. Animal-based foods (meat, fish, seafood) provide better absorption than plant-based ones, as plant foods contain phytates – compounds that reduce zinc bioavailability.
Factors Affecting Zinc Absorption
- Zinc Source
Animal-based products contain zinc in a more accessible form. - Presence of Phytates
Found in grains, legumes, and seeds, phytates bind to zinc and reduce its absorption. Soaking, fermenting, or sprouting these foods can lower phytate levels. - Concurrent Intake of Other Nutrients
Excess calcium, iron, or copper can hinder zinc absorption.
Tips to Improve Zinc Absorption:
- Pair zinc-rich foods with protein sources (e.g., meat).
- Limit phytate intake or properly prepare plant foods.
- Maintain a balanced diet.

Recommended Daily Zinc Intake
The daily zinc requirement varies based on age, gender, and physiological needs. A balanced diet usually meets these requirements, but supplements may be necessary in some cases.
- Adults: 10-15 mg/day (requirements increase during pregnancy and lactation).
- Children: 2 mg/day for infants to 11 mg/day for teens.
To correct a deficiency, supplement doses can increase to 20-30 mg for women and 30-45 mg for men.
High doses (>40 mg/day for adults) may be toxic and cause side effects, so adhering to recommended norms or consulting a doctor is essential before taking supplements, especially for children.

Choosing and Taking Zinc Supplements
Choosing zinc supplements depends on individual needs, supplement type, and preferred form. Here are some guidelines:
- Forms of Zinc
- Picolinate: One of the most effective forms due to its high bioavailability.
- Gluconate: Popular but may be less effective than picolinate.
- Acetate: Common in immunity-support supplements.
- Oxide: A more economical option but less bioavailable.
- Combined Supplements: Zinc paired with other minerals or vitamins (e.g., magnesium, vitamin C) for a broader impact.
- Dosage
The recommended dose for adults is typically 10–15 mg/day. High doses (>40 mg/day) may cause side effects like stomach upset, so consult a doctor before taking large doses. - When and How to Take
- Take zinc with food to reduce the risk of stomach irritation.
- Avoid taking it simultaneously with calcium or iron, as these minerals can reduce absorption.
- Zinc can lower the effectiveness of certain antibiotics and copper absorption.
- Brand Selection
- Reputation: Choose well-known and trusted brands that follow quality standards.
- Certification: Look for supplements tested in laboratories for quality assurance.
- Safety: Opt for supplements without harmful additives, such as dyes or artificial sweeteners.

Side Effects and Overdose Risks
While zinc is vital for normal body functions, excessive intake can lead to side effects.
Symptoms of Overdose:
Overdose occurs with doses exceeding the recommended 40 mg/day for adults. Symptoms include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Cramps
- Diarrhea
- Weakened immunity
- Increased “bad” cholesterol
- Anemia
Prostate Cancer Risk:
Some studies suggest that long-term zinc intake of over 100 mg/day may increase the risk of prostate cancer in men. While the mechanism is unclear, this underscores the importance of caution with high doses.
Interactions:
- Copper: Excess zinc can hinder copper absorption, potentially leading to a deficiency.
- Antibiotics: Zinc may reduce the effectiveness of certain antibiotics (e.g., tetracyclines and quinolones).
Top 5 Zinc Supplements from iHerb
Below are the TOP-5 zinc supplements with different dosages and forms, suitable for various needs of the body. These products have high ratings and positive reviews from users on iHerb.

Contains zinc bisglycinate, a highly absorbable form. Supports immunity, skin, and eye health. Users praise its quality and effectiveness.

Natural Factors, Zinc Chelate, 25 mg
High-quality chelated zinc ensures better absorption. Supports immunity, skin health, and metabolic balance. Vegan and non-GMO.

In citrate form, ensuring high bioavailability. Supports immunity, skin health, and reproductive function. Vegan-friendly and non-GMO.

Solgar, Zinc Picolinate, 22 mg
A highly bioavailable picolinate form. Promotes immunity, skin health, and reproductive function. Vegan and non-GMO.

Garden of Life, Vitamin Code, RAW Zinc
Derived from raw chelated brown rice. Minimally processed for higher bioavailability. Supports immunity, skin, and reproductive health. Vegan and non-GMO.
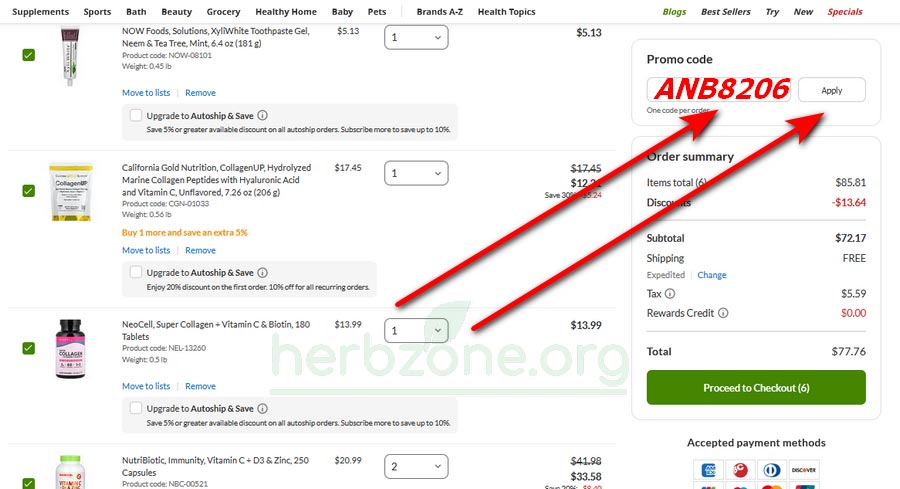
Enter the iHerb promo code ANB8206 to receive a discount of 5% to 30% on all your orders.
Use it an unlimited number of times – the discount applies to every purchase!